What is Pharmaceutical Validation, and Why is it Important?
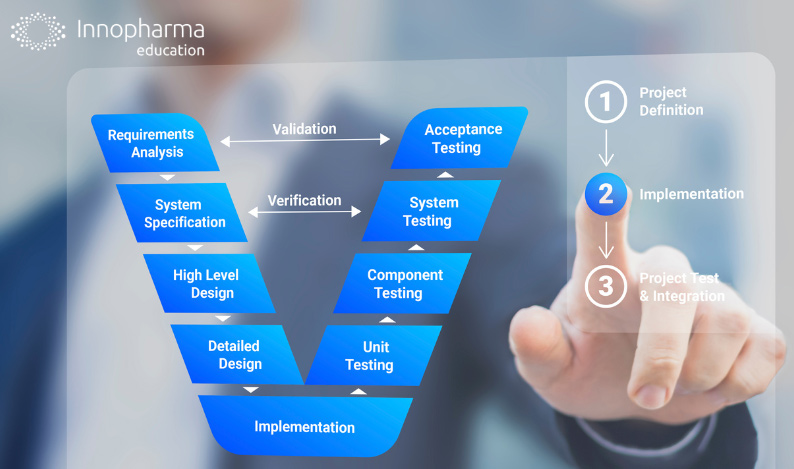
Pharmaceutical validation is an important process related to the pharmaceutical industry. It’s the means by which products are consistently produced and controlled to meet quality standards.
It’s a systematic process that verifies whether manufacturing processes, cleaning procedures, equipment, and analytical methods produce the desired results.
For an industry where precision and safety are of the utmost importance, understanding and implementing validation methods in pharma is an essential requirement. This article will explore the importance of validation in the pharmaceutical industry and the career opportunities it offers.
What is Pharmaceutical Validation?
Pharmaceutical validation is about establishing documented evidence to provide a high degree of assurance that a specific process will consistently produce a product meeting its specifications and quality attributes.
Key guidelines include:
- Quality by Design (QbD): Incorporating quality into the design of processes and products.
- Risk management: Identifying and mitigating risks throughout the production process.
- Lifecycle approach: Validation is an ongoing process that involves continuous monitoring and improvement.
- Compliance with regulatory standards: Adhering to guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), EMA (European Medicines Agency), and WHO (World Health Organisation).
- Documentation and traceability: Maintaining records to provide traceability and accountability.
It’s a component of the Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and regulatory requirements. Initially, the focus was primarily on end-product testing. However, with advancements in manufacturing technologies and the growing complexity of pharmaceutical products, there has been a shift towards validating the entire production process.
Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have developed stringent guidelines for comprehensive validation in the pharmaceutical and medical devices industry. They emphasise a proactive approach to quality control rather than a reactive one.
What are The Types of Pharmaceutical Validation?
Pharmaceutical validation is a broad field containing various different types of validation processes. Understanding these types helps to appreciate how comprehensive and meticulous the pharmaceutical industry must be to maintain high standards.
Process Validation
Process validation is the documented evidence that a manufacturing process consistently produces a product meeting its predetermined specifications and quality attributes.
Steps involved in process validation:
- Process design: Developing the process based on knowledge gained through development and scale-up activities.
- Process qualification: Confirm that the process design can be produced at a commercial scale.
- Continued process verification: Ongoing assurance that the process remains in a state of control during routine production.
Cleaning Validation
Cleaning validation ensures the cleaning procedures employed within a manufacturing facility effectively remove residues of the active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), excipients, and cleaning agents from the equipment and the environment.
Methods and standards used for cleaning validation
- Visual inspection: Ensuring no visible residues remain.
- Analytical testing: Using techniques like High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) to detect trace amounts of contaminants.
- Swab and rinse tests: Collecting samples from equipment surfaces to test for residual contamination.
Equipment Validation
Equipment validation verifies that the equipment used in manufacturing processes is installed correctly, operates as intended, and performs reliably to produce quality products.
Analytical Method Validation
Analytical method validation makes sure the analytical methods used to test pharmaceutical products are accurate, reliable, and reproducible.
Importance of Validation in The Pharmaceutical Industry
Validating is fundamental for maintaining confidence in the test results used to release pharmaceutical products to the market.
For example, it’s important that a High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) method accurately measures the concentration of an API in a drug product. This ensures that the product meets its specified potency and purity standards.
Product Quality
Validation is a core fundamental process for maintaining high product standards in the pharmaceutical industry. Involved is a series of rigorous tests and procedures designed to make sure that every aspect of the manufacturing process produces a consistent and reliable product.
Compliance and Regulatory Standards
Validation helps companies meet Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory requirements, which are designed to protect public health. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, including product recalls, fines, and loss of market approval, which can have significant financial and reputational impacts on a company.
Patient Safety
The primary goal of pharmaceutical validation is to ensure patient safety. By thoroughly validating manufacturing processes, cleaning procedures, equipment, and analytical methods, companies can prevent contamination, dosing errors, and other issues that could harm patients.
Cost Efficiency
While validation requires a significant upfront investment in time and resources, it offers long-term cost efficiency. Effective validation processes can reduce the likelihood of errors, product failures, and recalls, which are costly to address. By ensuring that equipment and processes operate correctly from the start, companies can avoid the expenses associated with rework and waste.
What Are The Key Processes in Pharmaceutical Validation?
There are many pharmaceutical validation techniques, including:
Validation Lifecycle (types of validation)
The validation lifecycle in pharmaceutical validation encompasses three main stages: Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ).
- Installation qualification (IQ): This stage involves verifying that equipment is installed according to the manufacturer’s specifications and design requirements.
- Operational qualification (OQ): During this phase, the focus is on testing the equipment and systems to ensure they operate according to the intended performance criteria.
- Performance qualification (PQ): This final stage involves verifying that the equipment and processes consistently produce products that meet all quality specifications during actual production conditions.
Documentation & Protocols
Documentation provides a detailed record of all validation activities and ensures traceability and accountability.
Key documents include:
- Validation Master Plan (VMP): This document outlines the company’s approach to validation, including the scope, objectives, and responsibilities for validation activities.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): SOPs are detailed, written instructions that describe how to perform specific validation tasks.
- Validation protocols and reports: These documents describe the specific procedures to be followed during validation and the results obtained.
Risk Management
Risk management helps to ensure that validation processes are fit for purpose and that any potential issues are addressed proactively.
- Risk assessment tools: Techniques such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) are used to identify potential risks and their impact on the validation process.
- Risk mitigation strategies: Once risks are identified, appropriate mitigation strategies are implemented to reduce their impact.
- Continuous monitoring and review: Regular audits and reviews help to identify new risks and ensure that existing mitigation strategies remain effective.
Career Path to Becoming a Validation Engineer
A validation engineer in the pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in ensuring that products meet all quality and safety standards.
Responsibilities may include:
- Developing and implementing validation protocols: Designing validation plans for processes, equipment, and methods.
- Conducting validation tests: Performing tests to verify that processes and equipment operate as intended.
- Documenting validation activities: Maintaining detailed records of drug validation processes and results.
- Ensuring compliance: Ensure all validation activities comply with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- Troubleshooting and problem-solving: Identifying and resolving issues that arise during validation to ensure consistent product quality.
Qualifications and Skills Needed
A Bachelor’s Degree in engineering, life sciences, chemistry, or a related field is typically required. Advanced degrees such as Postgraduate Diploma or Master’s Degree can be advantageous.
Beyond degrees, professional certifications, such as Certified Pharmaceutical Industry Professional (CPIP) or certifications from organisations like ISPE (International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering), can improve job prospects and demonstrate expertise.
Below are some of the skills expected of a validation engineer:
- Analytical thinking: Ability to analyse complex data and validate results to ensure processes meet predefined criteria.
- Attention to detail: Precision in executing validation protocols and documenting results is crucial for compliance and quality assurance.
- Problem-solving skills: Aptitude for diagnosing issues and implementing effective solutions during validation processes.
- Communication skills: Ability to clearly document validation activities and communicate findings to cross-functional teams.
- Regulatory knowledge: Understanding of regulatory requirements and industry standards to ensure compliance in all validation activities.
Salary Expectations
- Entry-level roles begin with validation technician and can expect to earn between €40,000 and €50,000 annually.
- Validation engineers with several years of experience typically earn between €50,000 and €70,000.
- Senior validation engineers and managers can earn upwards of €70,000 to €100,000 or more, depending on their level of expertise and responsibility.
Grow Your Career in Pharmaceutical Validation with Innopharma
Innopharma is a leading institution dedicated to providing high-quality education and training in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries.
At Innopharma, there is a wide range of training programs and courses specifically tailored to the pharmaceutical industry. Looking to embark on a career in validation? Join us for our BSc degree in Process Technologies, which covers the pharma, MedTech, and food industries.Take a step towards your validation goals with Innopharma Education. Contact us today for more information about studying at Innopharma.



















